23 mei Piri Reis – Türkiye
Learning To Become Active Citizens
In today’s democratic societies, the concept of active citizenship is gaining increasing importance. Active citizenship refers to the participation of individuals in social, political, and economic processes. This participation is critical for the healthy functioning of democracy. Active citizens have the ability to shape the future of their societies and take responsibility for sustainable development.
Active citizenship involves effectively participating in society, showing interest in public issues, contributing to political processes, and fighting for social justice in all its aspects. Our responsibility is not limited to voting in elections. Instead, it is vital for especially the younger generations to become active citizens to ensure the continuity of democratic values.
There are many ways to take part in society as an active citizen. These include, in addition to individual contributions, volunteering, participating in community organizations, making their voices heard in public spaces, contributing to local governments, and actively engaging in political processes. All these reflect individuals’ efforts to contribute to their communities and strengthen democratic values.
However, more efforts are needed to encourage active citizenship. Educational institutions, the media, and governments must play significant roles in raising awareness about this issue and encouraging individuals to participate. Education systems should be revised accordingly to ensure that especially young people grow up as active citizens.
In order to assume the role of raising active citizens, an educational institution may need to first transform its mission and vision. The inclusion of criteria for raising active citizens in the roadmap of an educational institution is crucial for planning subordinate activities towards this goal. With this perspective, Piri Reis Schools also renewed its mission and vision with the collaboration of all teachers and stakeholders in the 2021-2022 academic year.
Our vision was updated to help all individuals discover their potential in every area by considering their individual differences, to nurture their sense of curiosity, and to accompany learners on their journeys by creating a multilingual and multicultural school climate. Our mission was updated to cultivate universal individuals who are sensitive to sustainable living, have high self-respect, make a positive impact in their environment, carry their surroundings into the future, and internalize individual differences as richness.
Along with correctly defining the main framework such as mission and vision, it is important to follow the characteristics of generations, and changes in technology, social, cultural, political, and life aspects to raise active citizens.
Today, it is observed that more than 5 billion people are on social media. This number is increasing every day. This leads to the emergence of ethical and legal rules for a common life in this vast world.
Digital Citizenship in Piri Reis Schools
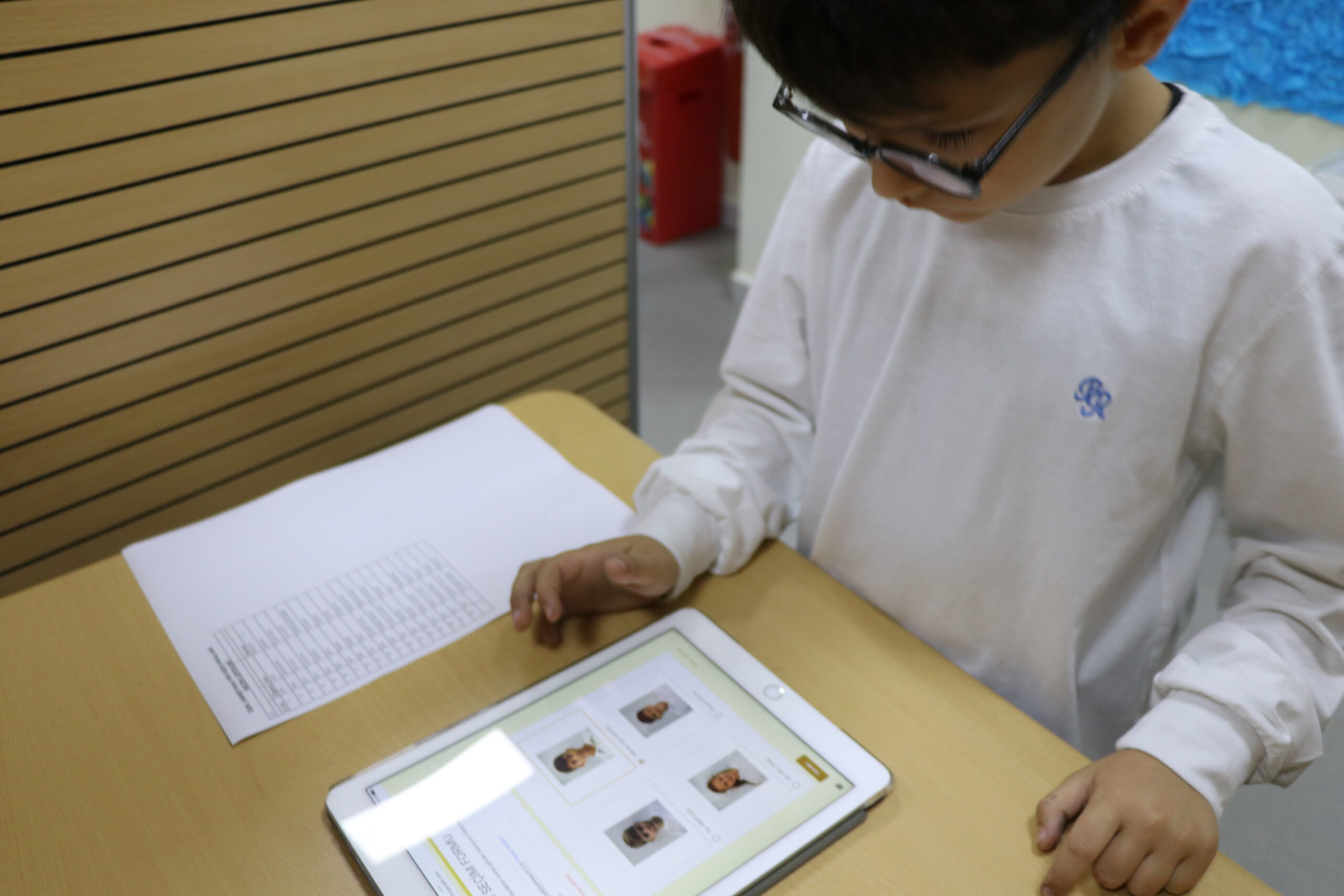
The necessity for expecting the citizenship skills we anticipate in real life to be expected in the digital world has arisen. Since 2015, a project has been implemented in our Piri Reis Schools to equip our students with digital citizenship skills. As part of this project, tablets are included in the formal education of our students. In the Digital Citizenship Education Handbook (2019) prepared by the Council of Europe, a digital citizen is defined as “a person who can actively, positively, and responsibly participate in both online and offline communities through a wide range of competencies.” Digital citizenship and participation encompass a wide range of activities, including creating, consuming, sharing, playing, socializing, researching, communicating, learning, and working.


Digital Citizenship and Its 9 Dimensions
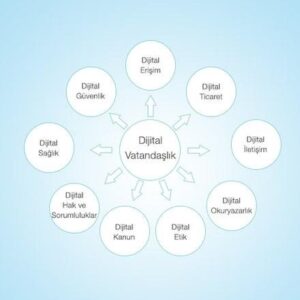
Educator Michael Ribble, in his book “Digital Citizenship in Schools: Nine Elements All Students Should Know” (2007), examined nine elements of digital citizenship to teach students to use digital technologies responsibly and effectively in schools. These are: digital access, digital commerce, digital communication, digital literacy, digital etiquette, digital law, digital rights and responsibilities, digital health and digital security. Our students are primarily being taught digital ethics, digital law, digital health, and digital literacy skills among the nine elements of digital citizenship. In this context, tablet usage rules are enforced both inside and outside the school. In research assignments, students are encouraged to question the accuracy of sources and use appropriate applications to promote digital literacy, behave ethically in the digital world to promote digital ethics, monitor usage time and receive addiction training from experts to promote digital health, and raise awareness about digital law through training provided by legal professionals.
In conclusion, we believe that for educational institutions to equip their students with active citizenship skills, it is effective to review and update their mission and vision and use elements of the world in which the new generation exists, considering their characteristics and interests.